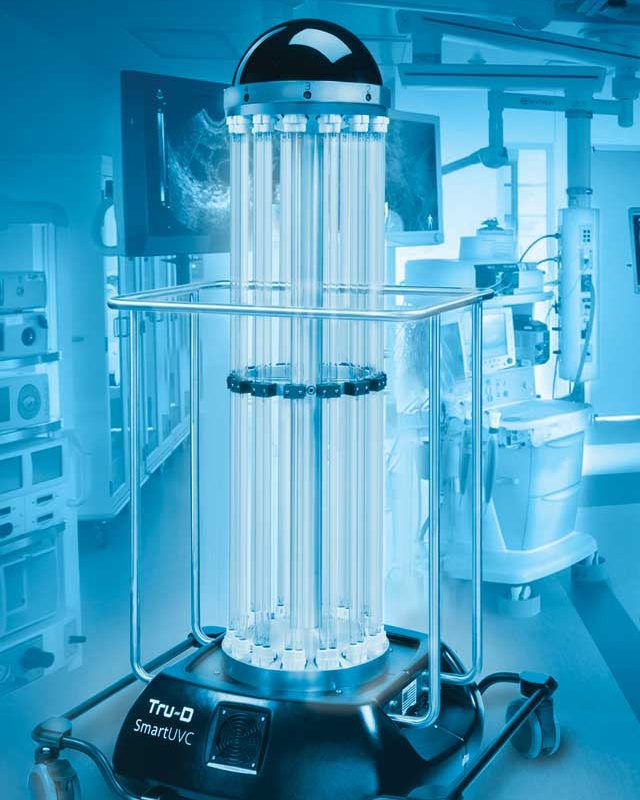
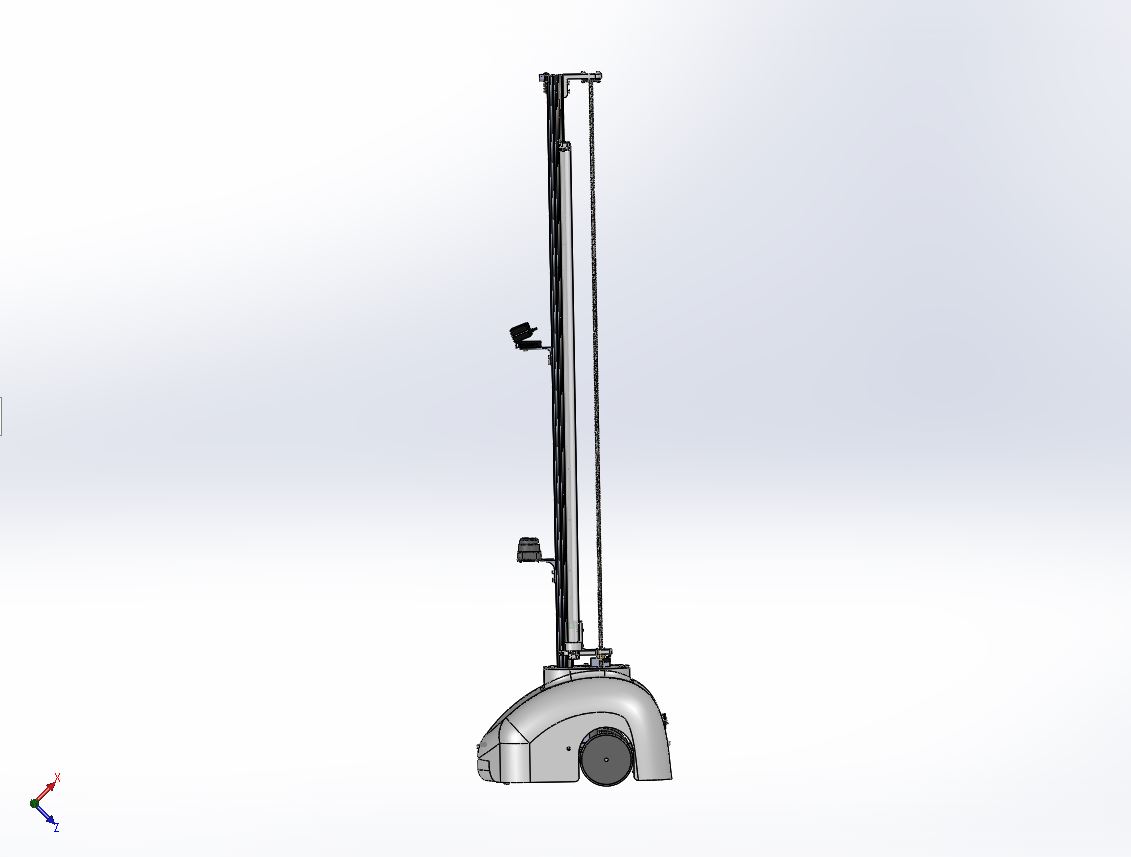
optimizing disinfection pathways for autonomous hospital cleaning robots
An extensive investigation into the feasibility of empowering autonomous sanitisation robots with path optimization algorithms to increase efficiency and safety.
About the Project
My Name is Nova Storm, a final year mechatronics and robotics student, and i am investigating using autonomous robots in healthcare. In healthcare settings, efficient and thorough disinfection is vital—but can autonomous robots do it better? This blog explores how path optimization algorithms can enhance sanitization robots by maximizing room coverage while minimizing time, energy use, and cost. Focusing on occupancy grids, gradient descent, and reactive sensor methods, we’ll dive into how smarter navigation boosts both efficiency and safety in hospital environments.

project outline
An autonomous hospital cleaning robot will be developed, tested, and validated successfully according to the project’s general planning, which takes a methodical, phase-by-phase approach. In order to determine system requirements, the project starts with a thorough study and planning phase that analyzes current robotic navigation techniques and disinfection procedures. After that, the development stage focuses on putting AI-driven path optimization algorithms into practice while combining UV-C light technology, depth sensors, and LIDAR for effective disinfection and navigation. Following the establishment of the essential features, the project proceeds to testing and simulation, using Gazebo and NX Siemens to assess performance prior to actual deployment. Improved effectiveness, flexibility, and a shorter disinfection time are guaranteed by the performance improvement process that follows.
defining problem
A well defined problem ensures focus and helps prevent wasted effort. It also allows for setting measurable goals, selecting the best approach, and allocating resources effectively.
research
Extensive research is conducted into Sterilisation in hospital environments and current path finding algorithms.
ideation
This marks the ideation stage, where existing solutions were evaluated, and a preliminary concept for the robot was developed.
design
Building on the concept from the previous stage, the robot was brought to life through detailed modeling.
Simulation
The modeled design is simulated in a hospital environment using ROS2 to test functionality and performance.
Refinement
An iterative approach is employed to continuously refine the simulation; after each test, results are analyzed, and improvements are implemented.
Cost and benefit analysis
The benefits of each method are analyzed based on efficiency, cost, and energy consumption.,
report and presentation.
Findings are finalized, and a comprehensive presentation and report are prepared to showcase the results.
Desired Project outcomes.
Maximized Coverage Efficiency
The algorithm should generate paths that maximize room coverage in the shortest time possible, ensuring thorough sanitization while minimizing redundant movements.
Optimal Use of Resources
The path optimization should balance energy consumption, battery life, and time efficiency, ensuring that the robot completes its task without running out of power too early or taking too long.
Sensor Integration and Reliability
The algorithm should seamlessly integrate sensor data (e.g., occupancy grids, distance sensors) to navigate dynamically and avoid obstacles or interference from the environment.
Improved Sanitation Effectiveness
Ensure the path planning optimizes sanitization coverage, with thorough disinfection in each room block, without missed areas or overlaps.
Robustness in Real-World Environments
This algorithm function reliably in diverse hospital room conditions, accounting for variations in layout, objects, and potential changes in the environment.
Deepened understanding
The process of developing the algorithm should deepen the readers understanding of the challenges involved with path optimisation.
-
Maximized Coverage Efficiency:
The algorithm should generate paths that maximize room coverage in the shortest time possible, ensuring thorough sanitization while minimizing redundant movements. -
Optimised Use of Resources
The path optimization should balance energy consumption, battery life, and time efficiency, ensuring that the robot completes its task without running out of power too early or taking too long. -
Reliably integrated sensor data
The algorithm should seamlessly integrate sensor data (e.g., occupancy grids, distance sensors) to navigate dynamically and avoid obstacles or interference from the environment -
Improved Sanitation Effectiveness
Ensure the path planning optimizes sanitization coverage, with thorough disinfection in each room block, without missed areas or overlaps. -
Robustness in Real-World Environments
It should function reliably in diverse hospital room conditions, accounting for variations in layout, objects, and potential changes in the environment. -
Deepened understanding
The process of developing the algorithm should deepen the readers understanding of the challenges involved with path optimisation.

| Phase | Task | Duration |
| Phase 1: Research and planning | Literature review on Hospital sanitisation techniques, defining scope. Algorithm planning methods. | 15 days |
| Phase 2: Existing Robot design Research and Ideation | Inspiration gathered from existing solutions. Concept design drawn up. | 9 days |
| Phase 3: Robot design (Solidworks) | Robot modelled on Solidworks | 9 days |
| Phase 4: Sensor and navigation integration | Integrating Sensors in simulated environment. | 8 days |
| Phase 5: Simulation and testing | Simulated environment setup fully. Gazebo and ROS used. | 15 days |
| Phase 6: Refinement and performance optimisation | Debugging, enhancing program. | 8 days |
| Phase 7: cost and feasibility analysis | Analysis of efficiency of algorithms and techniques | 7 days |
| Phase 8: Final report and presentation preparation | Compiling findings, presentation and report finalised. | 8 days |
| Phase 9: Proof reading, and review. | Final check. | 5 days |
Research
- A comprehensive literature review was conducted on sterilization processes in hospital environments, exploring various methods such as UV-C and gamma radiation. The review not only addressed key challenges in disinfection but also examined pathfinding algorithms and their effectiveness in dynamic settings. This dual focus offers an in-depth understanding of both sterilization requirements and optimization strategies for autonomous systems.


Ideation
- Several existing solutions were thoroughly examined for inspiration, focusing on their approaches to sterilization and path optimization. Both the strengths and weaknesses of these systems were carefully analyzed, highlighting areas for improvement and innovation. Based on these insights, a rudimentary concept for the robot was developed and visualized as a block diagram. This initial design laid the foundation for further refinement, outlining the key components and their interactions within the robot's architecture.
Design
- Several existing solutions were thoroughly examined for inspiration, focusing on their approaches to sterilization and path optimization. Both the strengths and weaknesses of these systems were carefully analyzed, highlighting areas for improvement and innovation. Based on these insights, a rudimentary concept for the robot was developed and visualized as a block diagram. This initial design laid the foundation for further refinement, outlining the key components and their interactions within the robot's architecture.


Simulation
- The modeled design is simulated within a hospital environment using ROS2 to assess its functionality and performance. RViz is employed for visualizing the robot's movements and sensor data, while various ROS plugins are utilized to enhance the simulation, ensuring that the system operates as intended in a dynamic, real-world setting.

Programming
- Several existing solutions were thoroughly examined for inspiration, focusing on their approaches to sterilization and path optimization. Both the strengths and weaknesses of these systems were carefully analyzed, highlighting areas for improvement and innovation. Based on these insights, a rudimentary concept for the robot was developed and visualized as a block diagram. This initial design laid the foundation for further refinement, outlining the key components and their interactions within the robot's architecture.
Testing
- Several existing solutions were thoroughly examined for inspiration, focusing on their approaches to sterilization and path optimization. Both the strengths and weaknesses of these systems were carefully analyzed, highlighting areas for improvement and innovation. Based on these insights, a rudimentary concept for the robot was developed and visualized as a block diagram. This initial design laid the foundation for further refinement, outlining the key components and their interactions within the robot's architecture.


Refinements
- Employing an engineering approach of continuous refinement and testing, the algorithm was iteratively improved with each cycle. Every iteration was carefully monitored, allowing for adjustments and enhancements based on real-time feedback and performance analysis.
Cost benefit analysis
- The benefits of each method are thoroughly analyzed in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and energy consumption, providing a clear comparison to determine the most optimal approach for the robot's performance.


Report and presentation
- The findings are consolidated and finalized, leading to the development of a comprehensive presentation and report to effectively convey the results, insights, and recommendations derived from the study. Potential areas for further investigation are also identified, providing a foundation for future research and outlining topics that could extend the scope and impact of this study.
tools used