In this section, various solutions are examined, with the best features being considered for my robot.
| Robot | Advantages | disadvtantages |
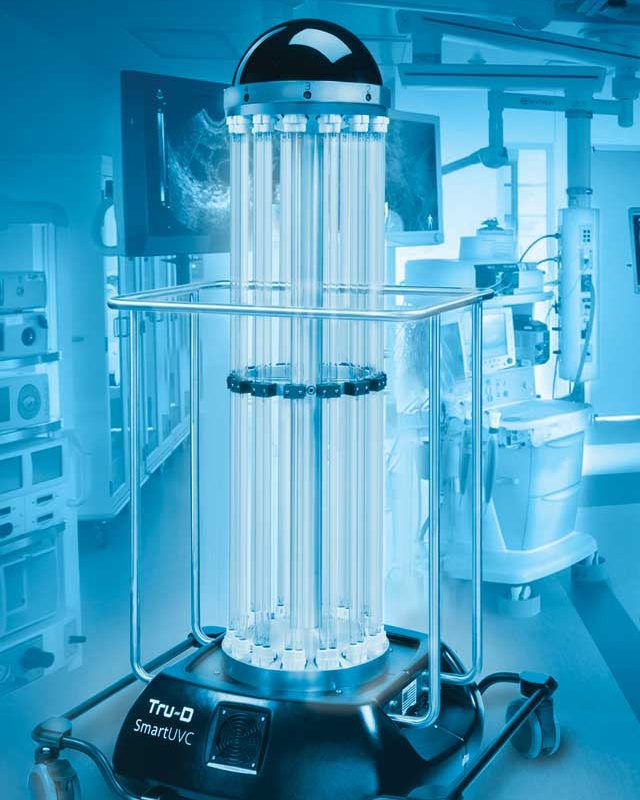
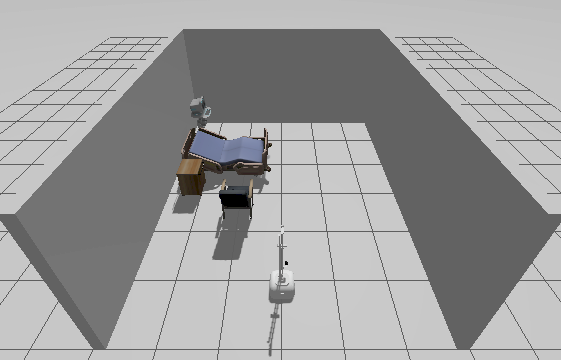
True-D |
Rapid chemical-free disinfection, effective against a wide range of pathogens, autonomous operation, high precision in targeted areas. | Requires empty rooms for safe operation, limited effectiveness in shadowed areas, high cost. |

Xenex |
Fast, chemical-free disinfection, adaptable for various room sizes, reduces HAIs, real-time monitoring. | High cost, requires clear paths for effective disinfection, cannot disinfect when rooms are occupied. |
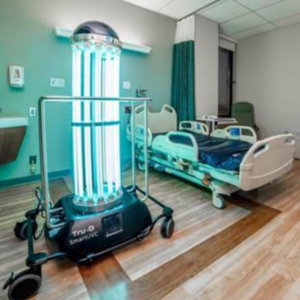
Mobile robot with 6 Dof arm. Arm would be replaced with UV-C lamp |
Highly flexible, precise movements, omni directional, would combat issue of shadowing. Versatile. | can be complex to program and integrate with other systems. Also the 6 DoF arm may be overkill for proposed issue. |

Similar to concept above, Light has replaced the arm |
Can get in more spaces than stationary robot. Smaller and more portable, easier and cheaper to produce.can navigate difficult environments, suitable for inspection and maintenance, | 6 Dof Arm will be complicated to program for given task. Smaller base means smaller battery and less battery life. |

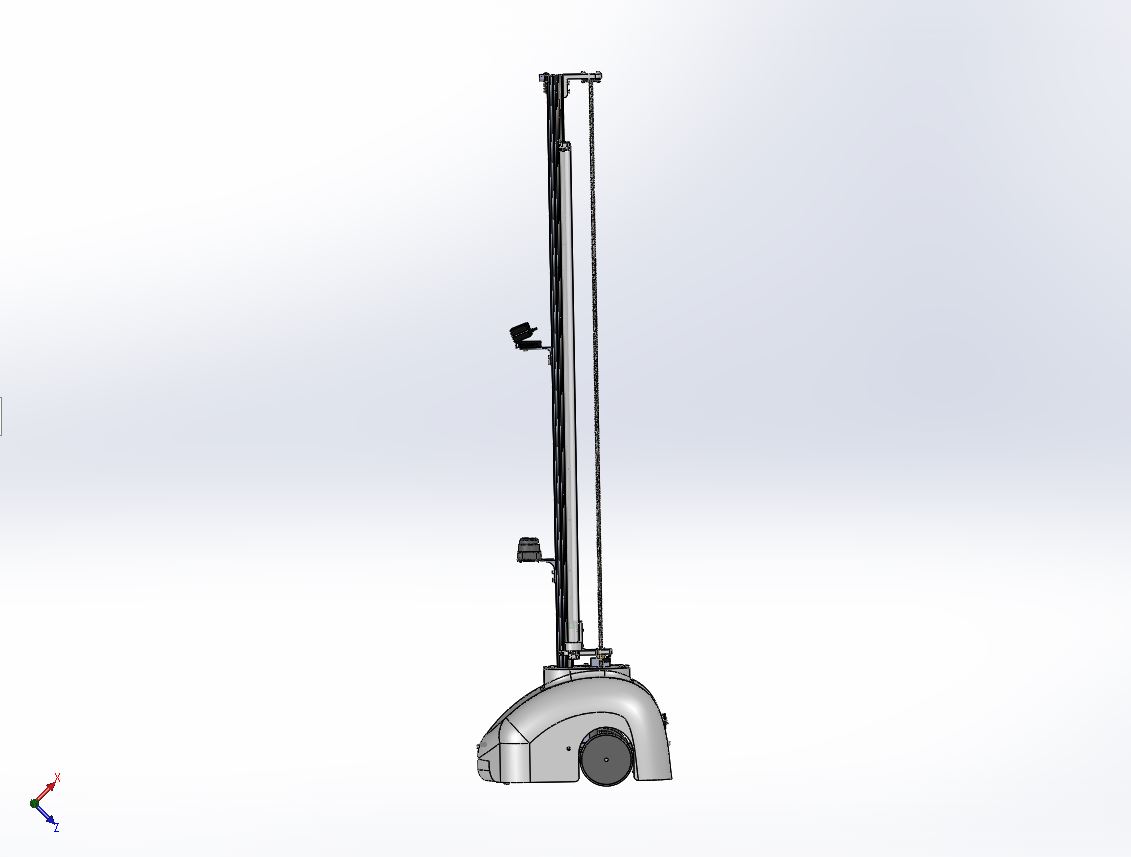
Similar to concept above, except arm is replaced by lamp with 1 DoF |
Lightweight, less complex and just as versatile as the light is getting in most places anyway. | Even though the lamp can be raised and lowered. There may be some scenarios where the rays cannot reach. |
More research was conducted on the best methods for robot localisation.
| Sensor Type | Operating Principle | Strengths | Weaknesses | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiDAR | Emits laser pulses and measures the time-of-flight of the reflected light to compute distances. | – High-resolution, accurate 3D mapping – Works in low-light conditions |
– Can be expensive – May struggle with transparent or highly reflective surfaces |
Autonomous vehicles, advanced robotics, mapping |
| Ultrasonic (Sonar) | Emits high-frequency sound waves and measures the time until an echo returns from nearby objects. | – Cost-effective and simple – Reliable for short-range detection |
– Lower resolution and range – Sensitive to soft materials and ambient noise |
Parking sensors, indoor robotics, simple obstacle detection |
| Infrared (IR) | Uses either active IR (emitting IR light and detecting its reflection) or passive IR (detecting heat signatures) for proximity detection. | – Low cost and low power consumption – Effective for very close-range detection |
– Limited range and resolution – Performance can be affected by ambient IR sources and reflective surfaces |
Proximity sensing, line-following robots, basic indoor obstacle avoidance |
| Cameras (Vision-based) | Captures visual data (color, texture) processed via computer vision algorithms for object detection and classification. | – Provides rich detail including color and texture – Capable of object classification and longer-range detection |
– Requires significant processing power – Performance can suffer in low-light or adverse weather conditions |
Autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, advanced robotics |
| Radar | Uses radio waves to detect objects, determine distance, and often gauge relative speed. | – Robust in adverse weather (fog, rain, dust) – Long-range detection |
– Generally lower spatial resolution compared to LiDAR and cameras – Can be expensive for high-resolution setups |
Automotive adaptive cruise control, industrial robotics, drones |
| Depth Cameras | Employ techniques such as structured light or time-of-flight (ToF) to capture both color and depth (3D) information of the scene. | – Provides both visual and depth data for enhanced object recognition – Enables 3D mapping at a relatively low cost compared to LiDAR – Useful for gesture and human detection |
– Limited range compared to LiDAR – Can be sensitive to lighting conditions and reflective surfaces – May require higher processing power to fuse depth with visual data |
Indoor robotics, augmented reality, gaming, human-computer interaction |
From this research , a combination of depth camera and a lidar sensor provided the best solution. As high resolution and reliability was needed for accurate localisation
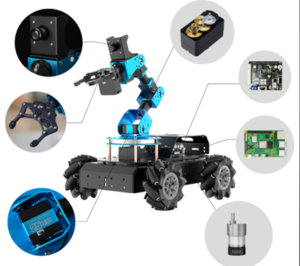
Using inspiration taken from this research. An initial block diagram was made, A block diagram is useful as it is very simple to make, and is just used to show where the components will go.
February 7th, 2025 3:11 pm